Foreword.
There’s this cartoon by, oh, let’s say Don Martin: a comedian on stage holds up a sign that says I’M FUNNY. —Noncommittal titters from the audience.
Next panel, the comic’s swapped signs for one that says YOU’RE FUNNY. The audience hisses and boos. (“It’s interesting to note,” says critic Marjorie Garber, “that the entities most usually described as ‘hissing,’ in the early modern period as also today, are devils, serpents, and audiences.”)
Third and final panel: the comic, dripping flop sweat, swaps signs one more time: THEY’RE FUNNY.
Cue the gales of laughter.
Every text is written in the first person.
Yes, all of them: even soi-disant experimental second-person narratives; especially those ostensibly in the third: every text is a first-person text. (Yes, and also those in the fourth. Hush, you.) —Every narrative must have a narrator, somewhere—did you check behind the curtain? If you’re still unclear, approach it as you would any other criminal enterprise: ask yourself, cui bono? Who chose the matter, wrangled the theme, pondered characters and angles of approach, began as they meant to go on? Such a constellation of considerations can’t help but cohere into a point of view, and that’s where, much as a sniper in a nest, you’ll find your narrator. (And if you shrug and say, with a quizzical cock to your brow, you mean the author? I’ll sagely shrug and answer back, perhaps.)
Once you’ve found the narrator, you’ve found your I in the sky: first mover, first shaker, first person.
“Did you notice?” said the Classicist. I don’t talk about the Classicist much, do I. And I have to be honest, here: while I remember having had the conversation, I don’t remember what we said, exactly, or where we were, not even a general sense of the circumstances, anymore. So let’s say we were having coffee in what I think was the only diner in town. “She pulled the whole thing off,” said the Classicist, with an emphatic gesture of her cigarette (menthol, which she would’ve bought next door, at what might’ve been called a bodega if we’d been in New York, but was called a bakery when the protests erupted years later), “the whole thing, without once telling you what was going on in anybody’s head.” —The SHE in that statement being Patricia McKillip, and the WHOLE THING being PULLED OFF the Riddle-Master books, and the statement itself not entirely correct, or right, or true: after all, when Morgon wakes up after the shipwreck, we’re told:
He tried to answer. His voice would not shape the words. He realized, as he struggled with it, that there were no words in him anywhere to shape the answers.
That’s from the first page of chapter three, and while it might be the first time we’re told something about someone’s state of mind that couldn’t be directly observed, or inferred from what’s been shown or told, it’s not the last. (And if you’d aver that the struggle described and the insight realized might well enough be inferred, perhaps by someone especially empathetic, I’d invite you past the next paragraph to read what follows: “A silence spun like a vortex in his head, drawing him deeper and deeper into darkness.”)
No, what the Classicist meant, if you’ll trust me to speak after all these years for her (and I’m not getting her voice right, not at all): in the writing of the Riddle-Master books, concerned as they are with identity, and selfhood, McKillip nonetheless eschews the free indirect: she never once presumes to speak for her characters, by making like their interiority’s seeping through the narrative. —You know. The bits Stephen King puts in italics. (Talking about King is probably how we got to this emphatic statement in the first place.) —Anyway. True or right or correct or not, it stuck with me.
Every narrative has a narrator. This may seem a ravelled tautology, but tug the thread of it and so much comes undone: a narrator, after all, is just another character, and subject to the same considerations. What might we consider, then, of a character who strives with every interaction for a coolly detached objectivity that’s betrayed by every too-deft turn of phrase? Who lays claim to an impossible omniscience, no matter how it might be limited, that’s belied by every Homeric nod? Who mimicks the vocal tics and stylings, the very accents of the people in their purview—whether or not they’re put in italics—merely to demonstrate how well it seems they think they know their stuff?
It’s only those texts that admit, upfront, the limitations and the unreliability of their narrators, that are honest in their dishonesty. —The third person, much like the third man, snatches power with an ugliness made innocuous, even charming, by centuries of reading protocols: deep grooves worn by habits of mind that make it all too lazily easy for an unscrupulous, an unethical, an unthinking author to wheedle their readers into a slapdash crime of empathy: crowding out all the possible might’ve beens that could’ve been in someone else’s head with whatever it is they decide to insist must have been.
The first few sketches of what would become (distractedly expansive gesture) all that were written on a clunky laptop lifted from an unlit room, filled with abandoned computers, just off the elevator lobby where I worked for a couple of weeks as a temporary receptionist. They were scraps of scenes, beginning after a beginning and never finding much of an end, but suggesting strongly where they’d come from, where they might go: our protagonist, Jo Maguire, already surly and underemployed, out for a night on the town with Becker, her gay best friend (making a stab or two at what would become his “epitome of mediocrity” speech); staggering back from the bathroom in time to see Ysabel, our protagonist, winding up the dancefloor with the slow-burn opening of Cassilda’s Song—only it was YSABEL, and BECKER, and JO, because these sketches all were written in screenplay form.
I was already writing a screenplay—it was why I’d stolen the laptop; some folks I knew were vaguely acquainted with a pot of techbro proceeds, and thought maybe a micro-budget horror film might prove an attractive tax shelter. It only made sense, when I was procrastinating the one, to sketch this incipient other in the same medium, and anyway, there’s room to play, in a screenplay, with voice, with performance, because the performance isn’t the point: it isn’t the final product, it’s instructions for assembling the final product. And who knew? Maybe I’d find some techbro money of my own (it was thicker on the ground, in those days), that might want to shelter itself in a micro-budget pilot for a syndicated television show. —My dreams were so much larger then, if simpler.
But the money went in another direction, and all I had to show for it was a screenplay no one would ever watch, and this, this thing that, if it was ever going to be anything, would have to become something else.
As I was considering how best to go about getting done what I wanted to do, I thought once more of the Classicist’s emphatic statement—maybe because these things had started as screenplays, concerned with the movement of bodies and objects in space, with words spoken out loud, not left to echo in somebody’s head—but I’d already played once or twice with the techniques suggested, in other, shorter pieces, elsewhere (much as writers today come up through fanfic, I’d done some time in the graduate seminars of alt.sex.stories.d). The strictures they impose—the pragmatics of blocking, the seamless exteriority, the relentless focus on precise, specific moments—that make it necessary to deal only by implication with what it is prose is supposed to excel at, by talking outside the glass: they can’t help but appeal to a scrupulous fool like me. So I decided to pull the whole thing off without ever once telling you what’s going on in anyone’s head.
But now I’m worried: having said this out loud, have I tipped my hand? Given the game away?
“I just don’t get it,” I said, and here we can suppose I gestured at the magazine on the table between us with a cigarette of my own (clove, filterless, bought at the drug store on the corner, where they kept the porn under a shelf behind the counter, so you had to ask for it).
“What’s not to get?” said the Classicist, and you have to understand, I would never have actually left such a thing lying out like that, but I have to have something to point to. Still: I did speak to her about this. This is another conversation that happened. Trust me.
“Well,” I said, and took a crackling drag. “If you had a sister. A twin. Would you do something like that?”
“Depends,” she said. Let’s say she sipped her coffee. “How much are they paying us?”
“But,” I said, “I mean, to, to take something, like that. I mean, whether you really feel it or not—actually, I think it might be worse if you faked it—but to take something like that and put it on display?”
“Honestly,” she sighed, “worse things happen at sea.”
Second seasons are where television programs typically hit their stride, confident in their logistics, but still gripped by their originating dreams. Second albums are sophomore slumps. Second movements are when things take a turn, get contemplative: usually scored andante or adagio, between fifty and seventy-five beats per minute, depending on your metronome. I’m not sure what can be said yet, about second series of epic urban fantasy webserial ’zines. There aren’t that many around from which to generalize.
This one is for the usual suspects, I suppose, but it’s also for the Classicist, who gave me if not the original idea, then a notion around which an idea might articulate itself. (You mustn’t blame her for any more than that.) But also, it’s for you. You’re the one reading this, after all.
In the Reign of Good Queen Dick
Portland, Oregon
2015 – 2019
1. THEY’RE FUNNY
2. I know you are
∴ But what am I

Three little words.
There was an episode, one of my favorite moments in Star Trek, when Captain Kirk looks over the cosmos and says, “Somewhere out there someone is saying the three most beautiful words in any language.” Of course you heart sinks and you think it’s going to be, “I love you” or whatever. He says, “Please help me.” What a philosophically fantastic idea, that vulnerability and need is a beautiful thing.
EDITH
And you don’t want to talk about it? Why? Did you do something wrong? Are you afraid of something? Whatever it is, let me help.KIRK
“Let me help.” A hundred years or so from now, I believe, a famous novelist will write a classic using that theme. He’ll recommend those three words even over I love you.
—The City on the Edge of Forever
The difference between “please, help me” and “let me help” is fairly dramatic. In Fry’s mismemory, Kirk seems almost to ghoulishly relish this cry for salvation, this opportunity to exercise his own benevolent power over someone in peril. In the actual quote, Kirk cites a novel we’ve not yet read, and the phrase itself is not a ventriloquised cry of need but a personal offer to serve.
KIRK
Why do you say that?EDITH
Sometimes you seem, well, disoriented, Jim, like a man just in from the country.KIRK
Iowa?EDITH
Further away than that.KIRK
“When night begins to fall, all men become strangers…”EDITH
It’s true. Who said it, I don’t recognize it.KIRK
Wellman 9. An obscure poet. Someday people will call his work the most beautiful ever known in the galaxy.EDITH
That’s a lot of territory.

Even the bull puts in some effort.
This piece—pleasant, but slight, ending just as it feels like it’s run through the pre-flight check for a much longer trip—does, at least (as it two-steps from of all things Paper Moon to the 48 Laws of Power), manage to articulate an essential, implacable truth of the Age in Which We’ve Found Ourselves Deposited: how on earth is it possible to speak as we so often do of Donald J. Trump as a grifter, when he can’t even be bothered to begin to pretend to try?

Mere strokes, interposed by a copyist.
There are rules to punctuation, of course, much as there are rules of grammar; the thing to keep in mind is that they’re descriptive, not prescriptive: technical documentation outlining specs, protocols, and use cases for an ancient system kludged together by oh so many divers hands, and as anyone can tell you, who’s ever had to document—and maintain said documentation for—anything at all: it’s forever going to be incomplete, inadequate, contradictory on the face of it, inexplicably controversial at unexpected points, and always always woefully out of date.
I mean, sure, yes: one uses a semicolon when joining two independent clauses that aren’t quite sentences of their own, given the broader context, when they can’t for whatever æsthetic be joined by a coordinating conjunction—but when I’m assembling sentences from key-clacks, I never not once do find myself thinking, ah, here’s two independent clauses, and no conjunction will do; let’s reach for a semicolon, shall we? —No: it’s the way the words fit one after the other, the heft of the passage in my mind’s hand, the lilt in my mind’s voice as it’s read back to my mind’s ear: this is what decides, for me, whether and when I reach for a semicolon, or an em-dash, or damn the torpedoes and splice the fuckers with a comma.
(A comma is where you take a breath, a semicolon is how the Welsh hedge the ends of declarations; a colon is more purposive: and thus turns neither up, nor down—the em-dash is a violent interruption, incorporated—and as for the ellipsis, well: it coyly trails…)
With the advent of the web, as writing and publishing carelessly merged, mixing the (supposed) iron science of grammar with the (presumed) mere craft of typesetting, use cases multiplied, and whole new arguments raged: whether to put two spaces after a full stop (if you’re displaying in a monospaced typeface? Sure!), or to italicize the punctuation at the end of an italicized phrase (opinions differ, as do fonts), or how best to set one’s em-dashes: there’s a school that would have spaces placed to either side whenever they’re deployed — like so; but to my eye that’s too much of an irruption in the color of the text on the page. Better by far to set them snug—like so; the flow, stuttered, is nonetheless maintained. Now: if you wished to use the en-dash instead (the width of the capital N in the font, or thereabouts, a touch more narrow than the width of the capital M: thus, em, and en, in dashes), you would deploy spaces to either side: the en-dash, being a touch more demure, would otherwise read as merely a hyphen. This technique, of an en-dash with spaces, is better than the em-dash in maintaining a consistency of color in blocs of text, but it’s not as versatile: the em-dash, if usually deployed without spaces, might here or there be employed with a space to the one side, or the other, at the end of a sentence, or the beginning: joining thereby sentences that aren’t quite separate paragraphs in much the manner a semicolon joins clauses that aren’t quite separate sentences. —But I digress.
This broader divagation we return to stems from a bit by Clive Thompson on “weird 19th-century punctuation marks you should try using,” which turn out not to be unusual new marks, but mere combinations: em-dash with comma, with colon, with semicolon. Thompson’s excited by the idea of playing with these ungainly chimeræ, and ordinarily I’d be as game as the next dingbat to put inconvenient extravagance to whatever use, but the commash, the colash, the semi-colash: or rather, perhaps:—or perhaps,—perhaps;—I just don’t feel it? Or rather, I do, I can, but the nuanced subtleties of the differences between each—and the constituent parts of each—it’s just too faint, too esoteric, to be worth their clumsy interpellations; I just, I’m afraid, don’t see—the point?
Thompson finds himself enchanted by the abrupt disappearance of these widespread, well-used hybrids, vanishing as they pretty much entirely did with the onset of modernism. He quotes the thirty-year-old (and rather better, because doubtless more amply compensated) Nicholson Baker essay that occasioned his bit:
What comet or glacier made them die out? This may be the great literary question of our time. I timidly tried to use a semi-colash in a philosophical essay for The Atlantic Monthly in 1983: the associate editor made a strange whirring sound in her throat, denoting inconceivability, and I immediately backed down. Why, why are they gone? Was it—and one always gropes for the McLuhanesque explanation first—the increasing use of the typewriter for final drafts, whose arrangement of comma, colon, and semi-colon keys made a quick reach up to the hyphen key immediately after another punctuation mark physically awkward? Or was it—for one always gropes for the pseudo-scientific explanation just after McLuhan—the triumphant success of quantum mechanics? A comma is indisputably more of a quantum than a commash. Did the point-play of the Dadaists and E. E. Cummings, and the unpunctled last chapter of Ulysses, force a scramble for a simpler hegemony against which revolt could be measured?
I mean, y’know, yeah? Sure. Why not? —It’s not as if there’s a single cause for this particular effect, a grand narrative here to be untangled and assembled beyond, I mean, you know, like we said: modernism. Even their names—commash, colash, semi-colash—are obvious excrescences easily trimmed in any drive to simplify, streamline, regularize and (yes) modernize. So they no longer fit with the heft of our words as we put them together, did nothing we found we needed to tune their lilt. They fell out of fashion. Which is no reason of course not to use them yourself, if you find you want to.
—As for myself, I’m much more taken by the notion mentioned in passing, in Baker’s essay, of punctuation as an emendation not by the writer, or the editor, or the publisher, but the reader—confronted by a bloc of monochromatic, undifferentiated, unspaced text, as it was written of old, might well take it upon themselves to
decorate a work with dots and diples and paragraph marks as they read it and then proudly sign their name on the page: “I, Dulcitius, read this.” Punctuation, like marginal and interlinear commentary, seems at times to have been a ritual of reciprocation, a way of returning something to the text in grateful tribute after it had released its meaning in the reader’s mind.
Well, that, and also a lingering puzzlement with those who insist on using guillemets as quotation marks. The hell is up with that? Seriously. It’s like, kkkttcht, every line of dialogue’s being spoken over a walkie-talkie or something, kkkttcht. —Over.

Kinematograph.
Then, what do we mean when we say “this is so cinematic!” There is of course the implication of the visual rendered in prose, but there is also, anecdotally, sometimes a level at which cinematic fiction also implies something about pacing or narrative rhythm or narrative composition—things that for my convenience I’ll group and condense into the term narrative depth. To be clear, I do not mean depth in the modern sense of a value judgement. I mean it in the sense of the distance between what is occurring in the narrative foreground and what is occurring in the narrative background, giving a sense of relief or contrast. In cinema, this contrast seems diminished. That is, in cinema, things are happening and there is less ostensible commentary upon the events or the psychology of the narrative. This is due to the nature of film as a medium. In prose fiction, there is a greater potential for contrast between event or incident and commentary, and one might say that cinematic fiction is fiction that emulates this lessened narrative contrast: the flattened narrative relief of cinema.
That’s from Brandon Taylor’s Miserly Eye, which makes some interesting points in the matter of cinematic fiction, and in a manner that doesn’t make me twitchy. I’ll continue to maintain, myself, that the primary distinctions ultimately stem from their respective mediums—that cinema’s dependence on images fixes it on specificities that prose’s narrow channel of one word after another can only approach with great effort—but I’ll spend some time thinking with this notion of depth of field, and Bellardi’s notion of foreground and background tenses, maybe.
In the meanwhile, it’s an excuse to index a number of old posts hereabouts on the matter: a couple of extended quotes from John Fowles; a brief divagation on why it is I might tend to twitch when the subject comes up; a disquisition on, well, it has more to do with comics and serialization, but it’s still pertinent to the work of translating the techniques of one medium into another; some consideration of less-than-obvious implications of a cinematic mode; and what I might maybe call the keystone piece. —So there’s that.


Hydriotaphia.
All these people everywhere whittering over how Midjourney AI and ChatGPT and whatnot mean computers or machine learning or artificial intelligence or whatever we’re calling it this week is on the verge of surpassing us all the rest of us when it comes to drawing or writing or pontificating or illustrating or designing or coding or bullshitting or doing our homework, and to be frank also all those people cheerfully playfully wickedly teasing the networks or inputs or weighted averages, or however it is it works, it’s all starting to remind me of nothing so much as what happens at the end of “Tlön, Uqbar, Orbis Tertius”—and you know what that means. Go on revising, in the quiet of the days; work as if you do not intend to see it published.

A good reality will parry the blow.
I don’t recall how I first heard of Helen DeWitt’s Last Samurai; I don’t have any longer that first copy (a Tina Brown Talk Miramax edition, I say, with an air of vaguely smugness); I think one of the many many times I lent it out it never made its way back, or I hope that’s the case, and it’s still vagabonding about, from hand to reading hand. (I’ve got a Chatto & Windus edition these days, which imprint was founded in 1855, then bought by Random House the year I graduated high school, then unceremoniously dumped under Vintage Books somewhere in the drafty halls of Penguin UK.) —I trust, at any rate, that the esteem in which I hold DeWitt is well known about these parts, and so you’ll understand I’ve just put in an order for Lee Konstantinou’s The Last Samurai Reread, about which I’ve only just found out.

In Memison, one must try the fish.
An exquisite little jewel of a review from M. John Harrison of a book that doesn’t exist so much in the particular, but very much in the aggregate; he comes at recent preoccupations hereabouts from other angles very much appreciated.

I mean the matter that you read, my lord.
Matter matter matter, let’s see—we’ve moved, across town, from Ladd’s Addition to Rose City; we’re homeowners now, and again, which means we can paint the rooms the colors we’d like, but also means we have to strip and sand and sweep and repair and replace and prime and tape and paint and paint again, over and over for each different color, and, well. Time passes. You look up and wonder what you’ve accomplished and then you look around, and yes, but also yes, well...
As for words words words: as to written, and here you must imagine me sucking my teeth. I’ve got the fortieth novelette queued up and ready to go starting Monday, but that’s the only one I’ve written this year, and last year I managed to write most of five, and the discrepancy gnaws. I’d point to the work alluded to in the paragraph above, and the work associated with the day job (turns out, preparing for and supporting a federal criminal trial? Time-consuming), but work we will always have with us, and the work still needs to get done, and the forty-first isn’t at the moment coming any faster, and as for anything written around here, well...
But as to have read, have been reading, to be read: currently bouncing between two big books, each expansively large in their own particular idioms: on the one hand, I’ve decided instead of dipping in almost at random to sample this run of stanzas, or that, to work my way through the F--rie Queene from first line to last, drawing what dry amusement I might from the coincidence in age between myself when I finally started it (53) and Virginia Woolf, when she finally started it (53)—
The first essential is, of course, not to read The F--ry Queen. Put it off as long as possible. Grind out politics; absorb science; wallow in fiction; walk about London; observe the crowds; calculate the loss of life and limb; rub shoulders with the poor in markets; buy and sell; fix the mind firmly on the financial columns of the newspapers, weather; on the crops; on the fashions. At the mere mention of chivalry shiver and snigger; detest allegory; and then, when the whole being is red and brittle as sandstone in the sun, make a dash for The F--ry Queen and give yourself up to it.
—only to find myself at the end of the first 12 cantos looking up, blinking, as our avatar of Holinesse, that Redcrosse knight his own dam’ self, so happy in his ever-after with Una, his one true only, the only one true only, suddenly just ups and leaves her in the space of eight lines of iambic pentameter and a single alexandrine—and, I mean, I know why St. George leaves the personification of true religion to return to F--ry Lond, but I can’t for the life of me figure out how Spenser knew, or at least what Spenser knew, and wanted me as a reader to know, and it’s another of those weird bucks and hitches from out of time that keep kicking me loose from the poem and yet drawing me back all at once.
The other is Pynchon’s Against the Day, which if I were feeling glib I’d describe as Roszak’s Flicker meets Vollmann’s Bright and Risen Angels with a dash of let’s say Matewan; it’s like the reading and research I did back in the day for that never-to-be-realized mashup of Blavatsky and Lovecraft, Space: 1889 and the Difference Engine, all was homework for enjoying this—but such flippancy isn’t meet for any of the works in question. It’s baggy and shaggy and too much by half, I’m completely lost every time I slip back into it, but comfortably lost, reliably at sea, and the stew of language Pynchon and Spenser make when taken in alteration is heady indeed.
Heady, but thick, and slow-going, and see above re: work, and so these other books are piling up in the queue: John Ford’s last book, and Avram Davidson’s last Virgil Magus book, Mary Gentle’s Ash, the Moonday Letters and the Monkey’s Mask, the Underground Railroad and a half-dozen Queen’s Thieves, and that’s just the fiction, good Lord, there’s the White Mosque which isn’t even on my shelves yet, and Reading and Not Reading the F--rie Queene, which is, but, I mean, well...
As for what I have read, recently, well, I mean, there was Under the Pendulum Sun, which was fine insofar as it went, some lovely and divertingly weird imagery, but overall the book’s preoccupations weren’t my own, or rather weren’t what I would’ve expected them to be, given what we’re given, which resulted in some unfortunate undercooking here and gauchely overdoing it there and left me mostly with I’m afraid a shrug; and then there was Jawbone, which was spectacularly taut and exactly pretty much what I wanted it to be until it somehow utterly failed to end; and then there was, well.
Oh, it’s a big thick wodge of an epic, diligently working the post-Martin space, which is terribly au courant for epics, and it’s got a killer title, and that’s about all I can say for it—it has nothing like Ojeda’s power, or Ng’s charm, it sags tiresomely when it doesn’t race through suddenly ancillary quests for plot coupons (I’m afraid my disdain is such I’ll reach for overused critical terminology): an Anthropologie®-curated fantasy with a girlboss gloss that insists I see a dragon without doing the work to show me anything like a goddamn dragon. —But Shannon did make two moves, at least, that stuck with me, in how they kicked me loose, but without anything beyond my own cussedness to draw me back:
The first (which, as I’m piecing this together, I realize happens second in the book, but it’s the first I remember, so) is when great revels are thrown to celebrate the introduction of Sabran, our unmarried cod-Elizabeth I, to her proposed suitor Livelyn, our cod-Anjou:
The Feast of Early Autumn was an extravagant affair. Black wine flowed, thick and heavy and sweet, and Lievelyn was presented with a huge rum-soaked fruit cake—his childhood favorite—which had been re-created according to a famous Mentish recipe.
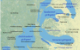
And at that I closed up the book, and looked about the bus (I was reading this almost entirely on the bus, in to work, and back home again), and then opened it up to the front to scour the maps—here, follow along—there’s the Queendom of Inys, or cod-England, and the Draconic Kingdom of Yscalin, or cod-Iberia, and the Free State of Mentendon, which I keep thinking of as cod-France, but is really more of a cod-Low Kingdoms (which makes doomed Lievelyn more of a cod–Holstein-Gottorp, I suppose); there’s cod-Lybia and a cod-Levant, and then over here on our other map we have wee cod-Nippon and but also the Empire of the Twelve Lakes, which is a cod-Middle Kingdom and not a cod-Minnesota—but what we don’t have is a cod-India, a cod-Cyprus, a cod-Madagascar, a cod-Madeira, a cod-Caribe, a cod-Hawai’i, not a cod-plantation to be seen—so when I read that a Prince’s favorite dessert is
a huge rum-soaked fruit cake
and you have countries and cultures and glimpses of history recognizably English and Spanish and Dutch and Japanese, and you tell me offhandedly you have rum, rum which if it is to be rum and not some phantastick honey liquor or something, but rum made from sugar, sugar from sugarcane (I mean, you can make rum from beet-sugar, but I’d hope you’d tell me it was beet-rum so I could take at least some visceral delight)—and sugarcane as such requires prodigious quantities of backbreaking labor to grow and harvest and process on a scale industrial enough to have enough left over to think to boil it into liquor, liquor enough that it might occur to a royal pâtissier, or banketbakker, to soak a fruitcake in a bottle’s worth to see what might come of it, you tell me that this is a thing in your world, but I look on your maps and I can’t anywhere find a trace of the God-damned Triangle—
—I’m gonna get flung right the fuck out.
The second move that stuck (which, again, now I’m looking at it, came first) is at once almost anticlimactically smaller and yet so very much more large: it’s a move made over and over throughout the book, but this was (for me, at least, at the time, for reasons) the most startlingly salient example, the one after which I could no longer ignore the bedevilment—it comes as Niclays Roos, disgraced alchemist and con artist, exiled before the novel begins from Mentendon to the lone Western trading post in Seiiki, our cod-Nippon, he’s being palanquined across the island to a mandatory meeting with the Warlord, and gets inexplicably dropped on his own in the middle of downtown Ginura, the Seiikinese capital, where he knows no one, nowhere, not hint of how to get to the Warlord, not a thing, until he coincidentally bumps into an old friend and colleague: Dr. Eizaru Moyaka, who, with his daughter, Purumé, had come some time before to Orisima, the aforementioned trading post, to study anatomy and medicine with this exiled Western doctor. Eizaru offers his modest house to Roos as a place to stay until the Warlord is ready, and Roos gratefully accepts; after all, he knows no one else here, nothing, no-how.
Eizaru lived in a modest house near the silk market, which backed onto one of the many canals that latticed Ginura. He had been widowed for a decade, but his daughter had stayed with him so that they could pursue their passion for medicine together. Rainflowers frothed over the exterior wall, and the garden was redolent of mugwort and purple-leaved mint and other herbs.
It was Purumé who opened the door to them. A bobtail cat snaked around her ankles.
“Niclays!” Purumé smiled before bowing. She favored the same eyeglasses as her father, but the sun had tanned her skin to a deeper brown than his, and her hair, held back with a strip of cloth, was still black at the roots. “Please, come in. What an unexpected pleasure.”
Niclays bowed in return. “Please forgive me for disturbing you, Purumé. This is unexpected for me, too.”
“We were your honored guests in Orisima. You are always welcome.” She took one look at his travel-soiled clothes and chuckled. “But you will need something else to wear.”
“I quite agree.”
When they were inside, Eizaru sent his two servants—
Wait—which the what, now?
We have a couple of academics living in a modest house—in the capital, on a canal, sure, nice little walled herb-garden, she’s answering the door herself, taking in an old friend on a whim, sure, but there’s a cat twining about her feet, and then, all of a sudden—servants?
This sudden, wrenching shift, the violent clash of assumptions, between what I’d expect of the class of a couple of modestly housed academics, worldly enough to travel to a distant, despised outpost for a chance to study with an exotically disreputable doyen, yet grounded enough to open their own door to visitors, and what the book was willing to prepare me to accept of their class, with the sudden irruption of these two servants, never named, never described, just there, to, to, I don’t know, to have done things, fetch water, keep the day’s heat at bay, lay out the food, deliver messages, to signal the class to which the doctors belong despite any other assumptions, to otherwise be ignored.
They’re of a piece, these similar ignorances: slipping a rum-soaked cake into a scene for the one set of connotations the word “rum” might bring, without taking into consideration all the others that freight the word; dropping a servant—two!—into a set-piece for no other reason and no other effect than that it is assumed servants of some sort must be there—a heedlessness severely detrimental to the building of a world.
But here’s me being awfully stern about an epic so—I’d say “slight,” I’d say “inconsequential,” but there’s stern again, and uncharitable. I mean, I did finish the dam’ thing, didn’t I? —And there, up above, did you catch it? When Virginia Woolf was telling us what we ought to do, and ought not do, before we set out to read the F--rie Queene? That we should “walk about London; observe the crowds; calculate the loss of life and limb; rub shoulders with the poor in markets—”
And who does it turn out to be are we, then, being addressed? And who, is it assumed, are not?

That mighty wall between us, standing high.
Over at Lawyers, Guns, and Money, Elizabeth Nelson presents a Jonbar hinge I never would’ve thought of: what if Merle Haggard had released “Irma Jackson” when he wrote it?


INT. HEADSPACE. DAY.
You know what’s really irksome about the Royal Tenenbaums?
It’s such an overtly, ostentatiously bookish film, from the inspiration for the grown-up whiz kids past their prime (everyone else will tell you it’s that Glass brood, but I’ll tell you it’s much more the ilk of Claudia and Jamie Kincaid and Turtle Wexler) to the obvious surface gloss of those exquisitely designed dust jackets, from the genially gravelly Narrator to the way it’s broken into chapters, with those primly typeset insertions—
—and there, that’s it, that’s what’s annoying: the text of the book we’re ostensibly reading as the movie unspools. If you read it (and it’s large enough to easily read, we’re given enough time), well. Ostensibility crumbles. —Oh, the first one, the Prologue’s okay: it’s just the Narrator’s opening lines, set down on the page and perfectly prosaic, excellently novelistic: “Royal Tenenbaum bought the house on Archer Avenue in the winter of his thirty-fifth year.” But the rest?
Chapter One as we can see starts off with “Royal’s suite at the Lindbergh Palace Hotel. There are shelves full of law books and hundreds of spy novels in stacks on the floor.” Chapter Four? “The side entrance of the hotel. Royal goes in through the revolving doors.” Chapter Seven? “The next morning. Richie comes downstairs. He carries the stuffed and mounted boar’s head.” The Epilogue? “A gentle rain falls in the cemetery, and the sky is getting dark.” —This isn’t the sort of prose to be found in books with those dust jackets, in novels written by Ellen Raskin or E.L. Konigsberg—these are passages from the screenplay of the movie that we’re watching, bald instructions to the production team, this is what needs to be seen to make the story happen, copied as-is and pasted just so, to lorem ipsum up a handful of grace notes in the movie’s art direction. Once you see it, you can’t unsee it, sticking out among all the other details so much more carefully considered. It irks.
I get a little twitchy, whenever the subject of cinematic writing comes up. —Cinematic writing, filmic writing, the screen-like æsthetic: here, let me grab a passage from Simon McNeil’s Notes on Squeecore, since that’s where I’m going to tell you it most recently came up:
Wendig is, perhaps, the clearest example of a novelist who writes in a filmic style. Now I think it’s important to draw out how I talked previously a bit about how this was a characteristic of Hopepunk—the mediation of a literary canon via its filmic representation being something I called out within the Hopepunk manifestos—but this isn’t so much a matter of Wendig mediating literature via its depiction on screens as it is Wendig drawing the screen structure back into the book. The crafting of an image becomes the chief concern of the novel in Wendig’s hands. Action is in the moment and the dialog is kinetic precisely because Wendig is trying to show his audience a moving picture rather than tell them a story. In a way the lionization of show, don’t tell, almost inevitably leads to the logic of a filmic literature. After all, internality often involves telling the audience how somebody feels. As “Show, Don’t Tell” becomes a hard rule, it’s not hard to see how an audience of would-be authors with an insufficient grounding in literature but a lot of exposure to television will inevitably interpret that to turn the page into a kind of screen.
Breezy, surfactant, imagistic, often in the immediately present tense and almost always the disaffectedly third person (first person in screen-like tips from teevee to vidya: first-person shooters, don’t you know): at its most amateurishly egregious, the iron law of SHOW DON’T TELL eats itself, as the prose insists on telling you the show that needs to happen in your head: bald instructions to the production team, as it were; passages cut and pasted from a screenplay. (Rather than show you a dinosaur, I tell you to see a dinosaur, to tie this to other ongoing threads.) —It can be intended as complimentary, to say of someone’s prose that it is cinematic, but there’s always a bit of English on the ball: oh, look, the writer’s trying so hard, the poor dear, to make prose do what it manifestly can’t—and anyway, everybody knows the book is always better than the movie. (Think of what it means, after all, what’s intended, when a television show is said to be novelistic.)
And, well, I mean, here’s me, then, and the epic: specifically imagistic, immediately present, disaffectedly third, cinematic, yes, okay, sure, filmic, all right, I’ll even cop to a screen-æsthetic, but only if I get to play with all the various meanings packed into “screen,” but but but I know what it is I’m doing, it’s not amateurish, honest, I’m sufficiently grounded and aware of if not all then at least a great many literary traditions—
See? Twitchy. And that’s never a good look on anyone.
I didn’t set down specific rules I’d follow, or at least not break, when I set out to figure out what I was going to do and be doing. It’s more that the rules assembled themselves, from what I wanted to pull off: an epically longform, episodic serial, and the best and most prevalent examples thereof at the time were superhero comics and hour-long dramedic television serials. So I leaned into that. —I’ve written before, about the differences between words, and moving pictures:
The primary difference between prose and cinema (beyond the obvious) is I think in time, and how each handles it; cinema (like theatre before it) no matter how achingly it might strive for universal generalities, must necessarily show you specific people doing specific things in specific places at very specific times. Prose, on its wily other hand, can say: “Monday morning staff meetings were always a chore for Willy” or “For the next week whenever she went to the coffee shop she saw the woman on the corner” or “And then everybody died.” —The narrow bandwidth of prose can’t begin to approach the wealth of incidental detail that makes up cinematic specificity without enormous slogging effort; most of the tricks and tips one needs to learn to tell stories and have them told with mere words, in fact, those reading protocols we’ve all had put in place, have everything to do with tricking us into thinking that specificity’s been achieved without us noticing (just as a great many of cinema’s tricks are all about forcing us to empathize with the saps up on the screen, bridging the vast gulf between their specificities and ours).
Setting out to ape the effects of one with the tools of another, though, is less about what I’m going to do (write with immediacy and specificity, as if, yes, I’m telling you what you’d see and hear if the story were playing out on a screen, yes yes) than what I won’t: generalize, pull back, sweep up and away from that immediate moment, that specific place. —And there’s one more thing prose does, that the epic does eschew:
Every narrative has a narrator. This may seem a ravelled tautology, but tug the thread of it and so much comes undone: a narrator, after all, is just another character, and subject to the same considerations. What might we consider, then, of a character who strives with every interaction for a coolly detached objectivity that’s betrayed by every too-deft turn of phrase? Who lays claim to an impossible omniscience, no matter how it might be limited, that’s belied by every Homeric nod? Who mimicks the vocal tics and stylings, the very accents of the people in their purview—whether or not they’re put in italics—merely to demonstrate how well it seems they think they know their stuff?
It’s only those texts that admit, upfront, the limitations and the unreliability of their narrators, that are honest in their dishonesty. —The third person, much like the third man, snatches power with an ugliness made innocuous, even charming, by centuries of reading protocols: deep grooves worn by habits of mind that make it all too lazily easy for an unscrupulous, an unethical, an unthinking author to wheedle their readers into a slapdash crime of empathy: crowding out all the possible might’ve beens that could’ve been in someone else’s head with whatever it is they decide to insist must have been.
I’d never presume to tell you what someone else is thinking, good Lord, no. That would be rude. Instead, I’m going to show you what it is they do, and say, and let you draw your own conclusions, and trust you to adjust them as we go.
Framing it this way, as what I’m not going to do, makes me mindful of the tools I’ve set aside, and turns those vasty fields untrampled into negative space—a very potent consideration in any composition: instead of showing you a dinosaur, or telling you to quick, think of a dinosaur, the hope is that these dotted moments, and the space implied between them, might at this moment or the next shiveringly resolve in your head into the suggestion, of a dragon-like, dinosaur-sylph—and all the more impactful, as it’s one you’ve made yourself.
A long way round, perhaps, but fitting, I think, for an idiom that seeks to immerse you in a slightly disjointed reality, to make you believe that at any moment a short sharp shock of the numinous might intrude. —At any rate: I’m having fun. The occasional twitch aside.
Actually, you know, the one for the epilogue’s okay, too? “A gentle rain falls in the cemetery, and the sky is getting dark.” That’s a fine-enough turn of phrase for a novel, or even a screenplay. Except of course for the fact that it’s not getting dark in the scene that then unfolds: the sky’s a fixed and dreary mid-afternoon. —The perils of adaptation, one supposes.

Civitas Aurelianorum.
So I’ve finally slowly been picking away at Treme, in part because I’m feeling a bit of a jones for some of the world below the Mason-Dixon, but mostly because I want that taste of systemically languid flânerie about a quintessentially urban warp and woof without, you know, all the fucking poe-leece the fucking Wire brings to the table (though there are still cops, of course there are cops, Jesus, the cops), and anyway: this point I’m making is entirely evanescent, but nonetheless: it is of some interest that the Baltimore of the Wire is, to the extent that it’s not only an inside joke, but a goddamn plot point, an insular world sufficient almost entirely unto itself, but—the New Orleans of Treme is almost from the very beginning dependent upon not nearly entirely but still to a surprising extent within the fiction coterminal with New York City. —But in the meanwhile, the car is making this very loud noise, and I’m supposed to be able to walk away from the day-job for a week-long vacation that involves a lot of driving just next week. But at least this verde margarita’s cold and spicy? At least.


In which, knowing nothing of necromancy—
I haven’t read Gideon the Ninth, and I’ll be upfront, here: I’m not all that likely to, which is really no skin off of anyone’s nose. This isn’t about Gideon the Ninth, or Tamsyn Muir, who I’m sure is a lovely person, for all I’ve never met or interacted with her. No: this starts off being about something somebody said to kick off a review of Gideon the Ninth:
A lot of the best recent science fiction and fantasy stories are notable for how well they color outside the lines. Disregarding genre expectations and freely borrowing tools from other literary traditions, a slew of writers are reinventing previously hide-bound forms. This is partially a progression of craft, but it’s also possible because of broader cultural phenomena—fantastical tropes, once restricted to a few niche markets, now dominate mainstream media. As a result, storytellers have to do less reinventing of the wheel each time they mix far-fetched elements—even the most general audiences don’t need the lore of vampires or zombies explained to them, so it takes very little narrative lifting to add such ghouls to an unexpected setting.
I’m not sure I can quite express how shiveringly wrong I find that passage, or the thought behind it, and I hasten to remind you that I haven’t read Gideon the Ninth, and so I cannot possibly be said to be saying that it is guilty of taking very little effort in its narrative lifting, just because it’s what someone else gestured toward when wanting to talk about it. —So I turn to what Paul Kincaid said, about another book I’m frankly not likely ever to pick up:
Actually, this use of language for effect rather than for sense, this notion that if you bundle enough images together somehow they will create an impression of something awesome, brings me to another problem I have with the story. There is a carelessness here that is evident both in the way the language is used and the story that the language is used to tell. When we are told, for instance, that “Red wins a battle between starfleets in the far future,” you wonder, given that the characters wander freely back and forth through time, what is meant by far future? Far future of what? That is thoughtless writing. But then, on the evidence of this story, I don’t think that either El-Mohtar or Gladstone has sat down to work out what a time war might be like and how it might be structured. Presumably Red and Blue are immortal (or at least as near immortal as makes no difference) agents who travel backwards and forwards through time changing events in order to create a different future that favours their side. So far so simple, but then Red tells us that “strands bud Atlantises to thwart her,” that 30 or 40 times she has walked away from a different sinking island. So there are multiple timelines; changing one event doesn’t change the future, it just births a new timeline. In which case, what are they fighting for? What could possibly constitute a victory, or a defeat, in such a situation. If everything goes wrong, then there is another timeline where everything has gone right. And if there can be no victory, there can be no cause for war. How do you go to war with an enemy who has just got everything they want in a different timeline? Over and over again throughout the novel I came up against the same notion: that none of this makes sense. There is a time war not because there is any functional purpose in the war, but because the authors need their two lovers to be on opposite sides in a conflict. This is Romeo and Juliet with two Juliets but otherwise no change: starcrossed lovers on either side of an age-old quarrel they cannot repair, needing to keep their affair secret, and leading to seeming death. Make the houses of Montague and Capulet into the enemy camps in a time war and lo you render the whole thing science fiction.
Which not only gets at the shortcomings of sidestepping such narrative lifting, but also demonstrates how pervasive that sidestepping is, or has been, or could become, in SF as it’s currently spoke, and begins to get at how frustrating those sidesteps can be, but, I mean, you don’t need me to tell you that, you saw WandaVision, right? —So I turn to what William Empson said, about old bad poetry: “This belief,” he said, of the notion that atmosphere—the taste left in the head—is all, and conveyed in some fundamentally unknowable way as a byproduct of meaning, independent of grammar, unsusceptible of analysis:
This belief may in part explain the badness of much nineteenth-century poetry, and how it came to be written by critically sensitive people. They admired the poetry of previous generations, very rightly, for the taste it left in the head, and, failing to realise that the process of putting such a taste into a reader’s head involves a great deal of work which does not feel like a taste in the head while it is being done, attempting, therefore, to conceive a taste in the head and put it straight on to their paper, they produced tastes in the head which were in fact blurred, complacent, and unpleasing.
The taste in the head—the sylph—is the shiveringly unspeakable concatenation of desire, doubt, belief, of wonder and of terror, brought on by seeing a dinosaur; one does not put down that taste merely by showing the audience a dinosaur. You can’t make me feel like I’m in a room with a vampire by telling me a vampire has entered the room. The narrative lift is all. —And if it turns out your narrative lifting is up to the task of making me feel the actual staggering weight of walking away from thirty or forty sinking Atlantises (why else reach for such overkill?), one after an apocalyptic other, or putting me in the same room as a snarkily magical génocidaire, well. —It’s not you, honest. It’s me. Maybe I’m getting old.

#HarshWritingAdvice.
I need you to understand when they tell you “The stakes aren’t high enough,” they don’t mean: make the stakes higher. Sweep it all up. Go big or go home. They mean, “Make me give a fuck already about what the hell’s already at stake.”